一 / 项目背景与相关案例
I. Project Background and Case Studies
数据中心热回收(Waste Heat Recovery)是将数据中心运行过程中产生的废热进行回收再利用的技术,可显著提升能源效率并减少碳排放。以下是国内外典型应用案例和技术方向:
Data Center Waste Heat Recovery is a technology that involves collecting and reusing the waste heat generated during the operation of data centers. It can significantly improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. The following are typical application cases and technical directions both domestically and internationally:
在国外,北欧的一些国家对数据中心余热进行回收利用。2011年,芬兰某公司研究通过不同的方式收集云计算数据中心产出的大量余热,并将其用于附近区域供暖,形成了良好的废热利用闭环。在芬兰和挪威等国家,部分地方政府与当地数据中心达成协议,将数据中心产生的热量购买并用于周边公寓的供暖。
Some Nordic countries recycle the waste heat generated by data centers. In 2011, a company in Finland explored various methods to capture the substantial waste heat produced by cloud computing data centers and utilized it for district heating in nearby areas, establishing an effective closed-loop system for waste heat recovery.In countries such as Finland and Norway, some local governments have reached agreements with data centers to purchase the heat generated by these facilities and supply it to surrounding apartments for heating purposes.
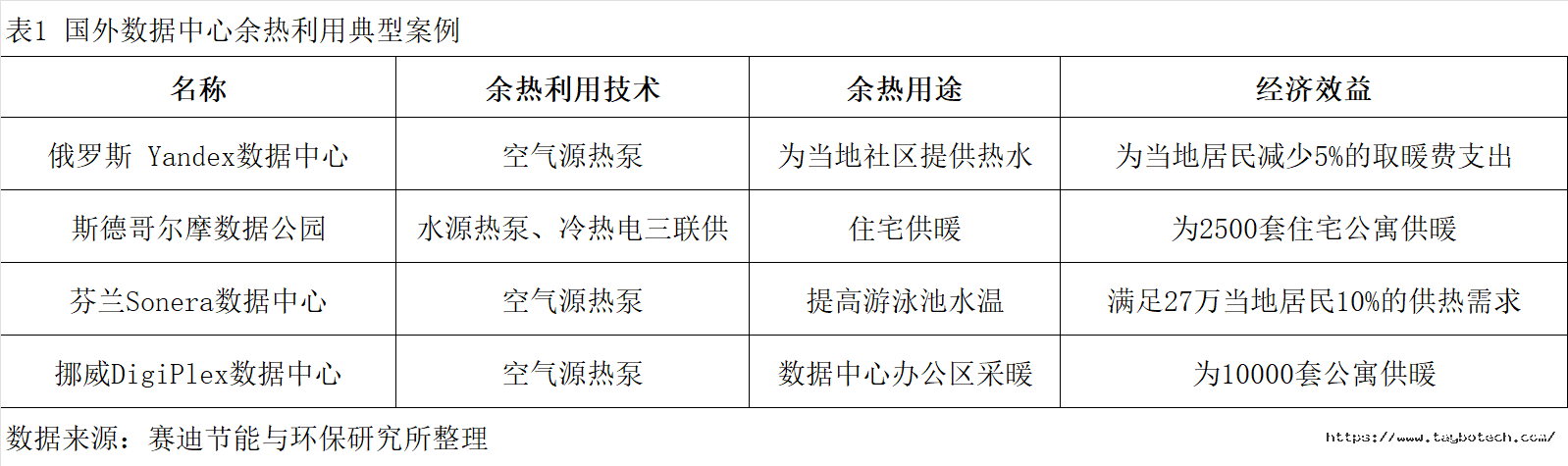
在国内市场,北京某热力集团将数据中心余热经水源热泵提升后,供给市政网直供及二次网供热。结果表明,可以产生巨大的经济效益和环境效益;某园区建设发展公司将数据中心的空调冷冻水作为热源,为附近办公楼供暖,并通过供热系统智能控制。
In the domestic market, a heating group in Beijing utilizes waste heat from a data center by elevating its temperature via water-source heat pumps, subsequently supplying it to the municipal primary network for direct supply and the secondary network for heating. The results indicate that this approach can yield significant economic and environmental benefits. Meanwhile, an industrial park development company uses the chilled water from a data center's air conditioning system as a heat source to provide heating for nearby office buildings, optimizing the process through an intelligent heating control system.
素材来源:制冷与空调,如涉侵权,联系删除
数据中心的总能耗中,制冷系统通常占 30%-40%,部分传统风冷数据中心甚至可能超过50%。
Within a data center's total energy consumption, cooling systems typically account for 30%-40%, with some traditional air-cooled data centers potentially exceeding 50%.
随着AI计算需求的增长,高密度服务器(如NVIDIA Blackwell架构GPU)的散热需求进一步增加,传统风冷系统的能耗问题更加突出。
With the growing demand for AI computing, thermal dissipation requirements for high-density servers(e.g., NVIDIA Blackwell architecture GPUs) continue to rise, making the energy inefficiency of traditional air-cooling systems increasingly pronounced.
二 / 项目概况
II. Project Overview
泰铂科技深耕数据中心热管理,特别是对现有数据中心节能改造有独特的见解和强大的技术支撑。应新加坡某App运营商邀请,泰铂科技因地制宜地为其定制了能源改造方案,在为业主节约电费的同时降低了碳排放,同时收到了额外的收益。
Taybo has deep expertise in data center thermal management, particularly excelling in energy-efficient retrofits for existing facilities. Invited by a Singapore-based app operator, we delivered a customized energy retrofit solution tailored to local conditions. This initiative not only reduced electricity costs and carbon emissions for the client, but also generated additional revenue streams.
新加坡某租用数据中心的企业,总机架数量65个,目前使用的机架数量为37个,每个机架的功率为8kW。为降低租用数据中心成本,特邀请泰铂为其定制能源改造方案。经过实地调研走访,发现数据中心邻近有一牛奶加工厂。该牛奶加工厂目前采用燃油锅炉为其巴氏杀菌工艺提供65-75℃热水,日用水量平均为78.4吨,每月的柴油费用约为29000新元。
A company leasing data center space in Singapore has a total of 65 server racks, 37 of which are currently in use, each with a power capacity of 8kW. To reduce data center leasing costs, the company specifically engaged Taybo to develop a customized energy retrofit solution. On-site investigations revealed that a milk processing plant is located adjacent to the data center. This plant currently uses a fuel-oil boiler to supply 65-75°C hot water for its pasteurization process, with an average daily consumption of 78.4 tons, resulting in monthly diesel costs of approximately S$29,000.
三 / 方案研讨阶段
III. During the proposal discussion phase
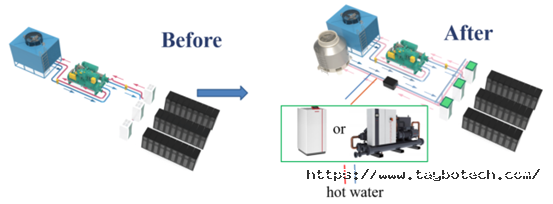
根据现有情况,泰铂科技提出了利用数据中心余热回收为牛奶加工厂提供热水的方案。将数据中心运行过程中产生的废热进行有效收集,并转化为可用于巴氏杀菌的热水。巴氏杀菌后降温则采用冷却塔散热,采用水源热泵在回收数据中心预热的同时回收此项预热。
Based on the current situation, Taybo has proposed a solution that utilizes waste heat recovery from the data center to provide hot water for the milk processing plant. The waste heat generated during data center operation is effectively collected and converted into hot water suitable for pasteurization. The cooling required after pasteurization is achieved through a cooling tower, while a water-source heat pump is employed to recover both the waste heat from the data center and this subsequent waste heat.
整套系统的运行由泰铂科技自主研发的CDU控制,其包含动力系统、电动三通阀和智能控制系统。该方案不仅减少了数据中心的冷却能耗,还为牛奶加工厂节省了燃油锅炉的运行成本。
The entire system is operated by the CDU independently developed by Taybo, which includes a power system, electric three-way valves, and an intelligent control system. This solution not only reduces the cooling energy consumption of the data center but also saves operational costs of the fuel oil boiler for the milk processing plant.
四 / 节能效益测算
IV. Energy Savings Assessment
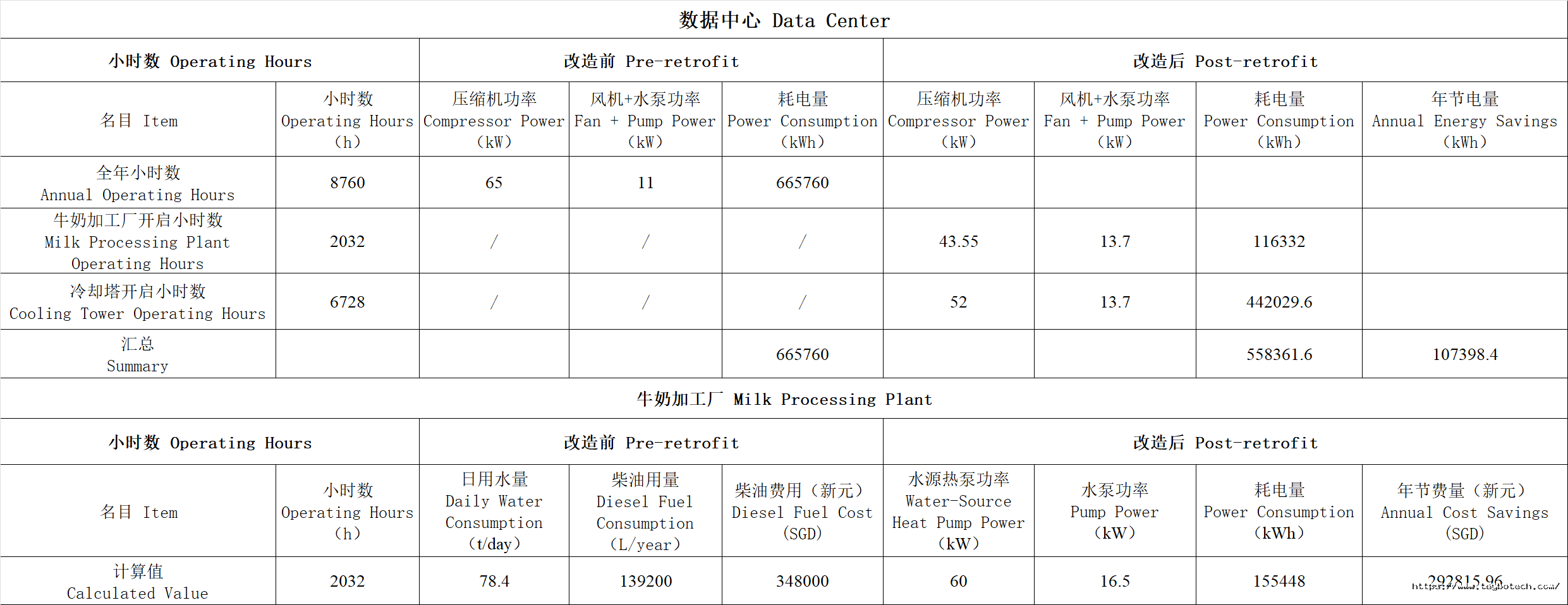
经测算,实施改造后,数据中心的年节约用电量为10.7万kWh,年节约费用3.8万新元(电费单价0.355新元/kWh),减少碳排放43.5吨;牛奶加工厂年节约柴油139200L,增加热泵与水泵耗电155448kWh,共计节约运行费用29.3万新元,减少碳排放310吨。本项目共减碳量353.5吨,节约运行费用33.1万新元。
After the implementation of the transformation, it is calculated that the annual electricity savings of the data center amount to 107,000 kWh, with an annual cost savings of S$38,000 (electricity cost per kWh is S$0.355), and a reduction in carbon emissions of 43.5 tons. The milk processing plant saves139,200Lof diesel annually, while increasing electricity consumption for heat pumps and water pumps by 155,448 kWh, resulting in a total operational cost savings of S$293,000 and a reduction in carbon emissions of 310 tons. The total carbon reduction of this project is353.5 tons, with operational cost savings of S$331,000.
附表:节能改造估算表
Appendix: Energy Retrofit Cost-Benefit Estimation Sheet
备注:出于对客户信息保密,以上案例公开数据或有调整